This chapter explains how Hazelcast is supported on OSGI (Open Service Gateway Initiatives) environments.
OSGI Support
Hazelcast bundles provide OSGI services so that Hazelcast users can manage (create, access, shutdown) Hazelcast instances through these services on OSGI environments. When you enable the property hazelcast.osgi.start (default is disabled), when an Hazelcast OSGI service is activated, a default Hazelcast instance is created automatically.
Created Hazelcast instances can be served as an OSGI service that the other Hazelcast bundles can access. Registering created Hazelcast instances behavior is enabled by default; you can disable it using the property hazelcast.osgi.register.disabled.
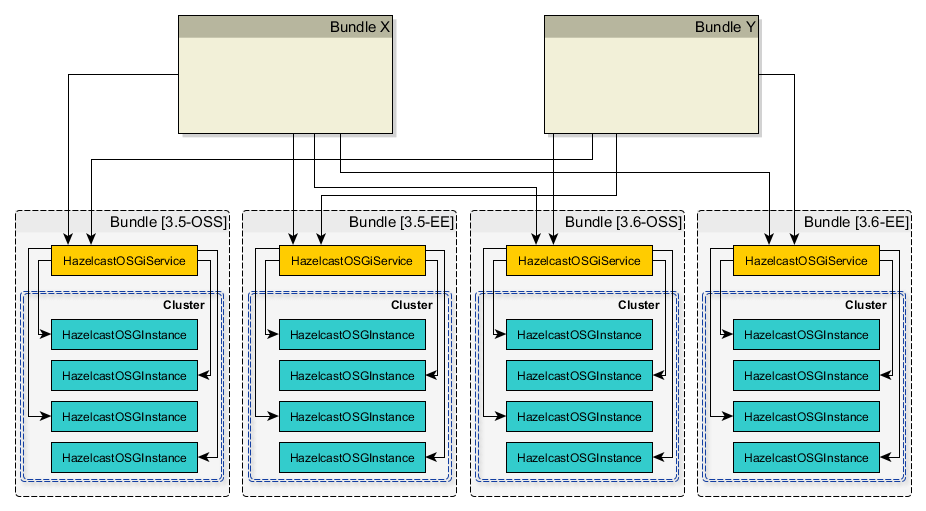
Each Hazelcast bundle provides a different OSGI service. Their instances can be grouped (clustered) together to prevent possible compatibility issues between different Hazelcast versions/bundles. This grouping behavior is enabled by default and you disable it using the property hazelcast.osgi.grouping.disabled.
Hazelcast OSGI service's lifecycle (and the owned/created instances's lifecycles) is the same with the owner Hazelcast bundles. When the bundle is stopped (deactivated), the owned service and Hazelcast instances are also deactivated/shutdown and deregistered automatically. When the bundle is re-activated, its service is registered again.
The Hazelcast IMDG Enterprise JAR package is also an OSGI bundle like the Hazelcast Open Source JAR package.
API
HazelcastOSGiService: Contract point for Hazelcast services on top of OSGI. Registered to org.osgi.framework.BundleContext as the OSGI service so the other bundles can access and use Hazelcast on the OSGI environment through this service.
HazelcastOSGiInstance: Contract point for HazelcastInstance implementations based on OSGI service. HazelcastOSGiService provides proxy Hazelcast instances typed HazelcastOSGiInstance which is a subtype of HazelcastInstance and these instances delegate all calls to the underlying HazelcastInstance.
Configuring Hazelcast OSGI Support
HazelcastOSGiService uses three configurations:
-
hazelcast.osgi.start: If this property is enabled (it is disabled by default), when anHazelcastOSGiServiceis activated, a default Hazelcast instance is created automatically.
-
hazelcast.osgi.register.disabled: If this property is disabled (it is disabled by default), when a Hazelcast instance is created byHazelcastOSGiService, the createdHazelcastOSGiInstanceis registered automatically as OSGI service with type ofHazelcastOSGiInstanceand it is deregistered automatically when the createdHazelcastOSGiInstanceis shutdown.
-
hazelcast.osgi.grouping.disabled: If this property is disabled (it is disabled by default), every createdHazelcastOSGiInstanceis grouped as their ownerHazelcastOSGiServiceand do not join each other unless no group name is specified in theGroupConfigofConfig.
Design
HazelcastOSGiService is specific to each Hazelcast bundle. This means that every Hazelcast bundle has its own HazelcastOSGiService instance.
Every Hazelcast bundle registers its HazelcastOSGiService instances via Hazelcast Bundle Activator (com.hazelcast.osgi.impl.Activator) while they are being started, and it deregisters its HazelcastOSGiService instances while they are being stopped.
Each HazelcastOSGiService instance has a different service ID as the combination of Hazelcast version and artifact type (OSS or EE). Examples are 3.6#OSS, 3.6#EE, 3.7#OSS, 3.7#EE, etc.
HazelcastOSGiService instance lifecycle is the same with the owner Hazelcast bundle. This means that when the owner bundle is deactivated, the owned HazelcastOSGiService instance is deactivated, and all active Hazelcast instances that are created and served by that HazelcastOSGiService instance are also shutdown and deregistered. When the Hazelcast bundle is re-activated, its HazelcastOSGiService instance is registered again as the OSGI service.
Getting Hazelcast OSGI Service Instances
You can access all HazelcastOSGiService instances through org.osgi.framework.BundleContext for each Hazelcast bundle as follows:
for (ServiceReference serviceRef : context.getServiceReferences(HazelcastOSGiService.class.getName(), null)) {
HazelcastOSGiService service = (HazelcastOSGiService) context.getService(serviceRef);
String serviceId = service.getId();
...
}
Managing and Using Hazelcast instances
You can use HazelcastOSGiService instance to create and shutdown Hazelcast instances on OSGI environments. The created Hazelcast instances are HazelcastOSGiInstance typed (which is sub-type of HazelcastInstance) and are just proxies to the underlying Hazelcast instance. There are several methods in HazelcastOSGiService to use Hazelcast instances on OSGI environments as shown below.
// Get the default Hazelcast instance owned by `hazelcastOsgiService`
// Returns null if `HAZELCAST_OSGI_START` is not enabled
HazelcastOSGiInstance defaultInstance = hazelcastOsgiService.getDefaultHazelcastInstance();
// Creates a new Hazelcast instance with default configurations as owned by `hazelcastOsgiService`
HazelcastOSGiInstance newInstance1 = hazelcastOsgiService.newHazelcastInstance();
// Creates a new Hazelcast instance with specified configuration as owned by `hazelcastOsgiService`
Config config = new Config();
config.setInstanceName("OSGI-Instance");
...
HazelcastOSGiInstance newInstance2 = hazelcastOsgiService.newHazelcastInstance(config);
// Gets the Hazelcast instance with the name `OSGI-Instance`, which is `newInstance2` created above
HazelcastOSGiInstance instance = hazelcastOsgiService.getHazelcastInstanceByName("OSGI-Instance");
// Shuts down the Hazelcast instance with name `OSGI-Instance`, which is `newInstance2`
hazelcastOsgiService.shutdownHazelcastInstance(instance);
// Print all active Hazelcast instances owned by `hazelcastOsgiService`
for (HazelcastOSGiInstance instance : hazelcastOsgiService.getAllHazelcastInstances()) {
System.out.println(instance);
}
// Shuts down all Hazelcast instances owned by `hazelcastOsgiService`
hazelcastOsgiService.shutdownAll();
